Key Differences Between Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets, though seemingly similar, play pivotal roles in various industries, including automotive and aerospace, each ensuring optimal performance and safety through distinct functions.
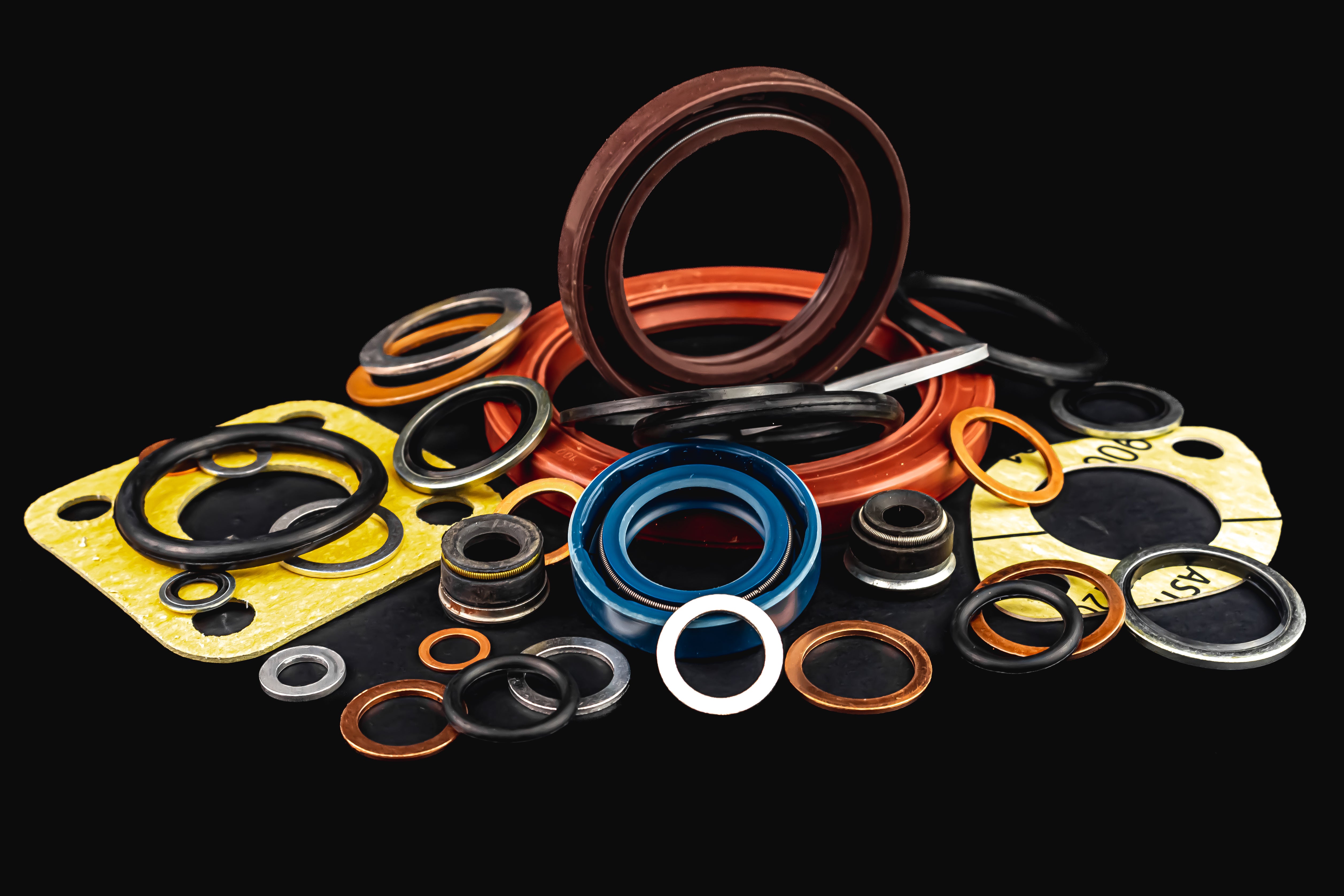
Seals, such as shaft seals and oil seals, prevent fluid or gas escape between dynamic surfaces. Gaskets, serving as a second barrier, are used between flat surfaces like outer rings and inner surfaces to avert leaks. While it is true they perform similar functions in preventing leaks, gaskets and seals have distinct applications. As we delve into their world, it's crucial to recognize and understand the key differences that set seals and gaskets apart, highlighting their unique contributions in maintaining system integrity.
With nearly five decades of industry experience in manufacturing auto detailing equipment and supplies, MTM Hydro Parts powered by Veloci boasts a wide range of premium seals and gaskets; feel free to check them out.
Defining Seals and Gaskets: Exploring Their Unique Characteristics and Functions

Seals and gaskets, despite their similar purpose of preventing leaks, differ in their design and function. Seals are often made of materials like rubber or metal and are specifically crafted to create a tight barrier between two moving surfaces, such as shafts or pistons. Their primary goal is to prevent the escape of fluids or gases in order to maintain system efficiency.
On the other hand, gaskets are typically composed of softer materials like rubber, paper, or cork, and serve as static seals. They are placed between two stationary surfaces to prevent leaks from occurring at the junction point. Gaskets are generally thicker and larger than seals, allowing them to cover a wider surface area. This broader coverage helps to distribute pressure evenly, ensuring a secure seal and minimizing the risk of leakage.
Seals and gaskets also differ in terms of their application. Seals are commonly found in dynamic systems where there is movement between two components, such as engines or pumps. Their ability to withstand friction and wear makes them ideal for these high-performance applications.
On the other hand, gaskets are primarily used in static systems where there is little to no movement between surfaces, such as flanges or pipe connections. Their main objective is to create a reliable seal, even in the absence of movement. This makes gaskets an essential component in industries like plumbing, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace.
Key Differences Between Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets, although serving a similar purpose of preventing leaks, have distinct differences in their design, function, and application.
Design:
- Seals are typically made of rubber or metal and are tailored to create a tight barrier between moving surfaces.
- Gaskets, on the other hand, are usually composed of softer materials like rubber, paper, or cork and serve as static seals.
Function:
- Seals are used to prevent the escape of fluids or gases in dynamic systems where there is movement between components.
- Gaskets, being larger and thicker than seals, cover wider surface areas and provide a secure seal in static systems, minimizing the risk of leakage.
Application:
- Seals are commonly found in engines, pumps, and other high-performance systems that require resistance to friction and wear.
- Gaskets are primarily used in plumbing, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace industries to create reliable seals in flanges or pipe connections.
When to Replace Seals and Gaskets?

Knowing when to replace seals and gaskets is crucial to maintain the integrity and efficiency of systems. While both play a vital role in preventing leaks, their lifespans may vary due to factors such as material quality, usage conditions, and maintenance.
For seals:
- Regular inspection: Check for signs of wear, cracks, or damage.
- Fluid or gas leakage: If there is noticeable leakage despite proper lubrication, it may be time for a replacement.
- Reduced performance: If there is an increase in friction or decrease in system efficiency, it could indicate seal deterioration.
For gaskets :
- Visual inspection: Look for signs of compression set, tearing, or deformation.
- Leakage: If there are leaks around flanges or connections despite proper installation and tightening, it may be necessary to replace the gasket.
- Temperature and pressure sensitivity: Gaskets that are exposed to extreme temperatures or high-pressure conditions may degrade faster and require more frequent replacement.
- Age and maintenance history: Older gaskets or those that have not been properly maintained may be more prone to failure and should be replaced as a precautionary measure.
Overall, it is important to establish a regular maintenance schedule for seals and gaskets to ensure the continued functionality of systems that rely on them for resistance to friction and wear.
How to Choose Between a Seal and a Gasket?

When it comes to choosing between a seal and a gasket, there are a few factors to consider. Firstly, you need to determine the specific purpose and requirements of your application. Seals are typically used in dynamic environments where there is motion involved, such as in rotating machinery or hydraulic systems. On the other hand, gaskets are more commonly used in static applications where there is no movement, like flange connections or pipe joints.
Another important consideration is the material compatibility with the substance being sealed. Seals and gaskets come in various materials such as rubber, silicone, metal, or composite materials such as graphite or PTFE. It is crucial to choose a material that is compatible with the fluid or gas being sealed to ensure optimal performance and prevent any chemical reactions or leaks.
Additionally, the temperature and pressure conditions of the application should be taken into account. Seals and gaskets have different temperature and pressure ratings, so it is important to select one that can withstand the specific conditions of your system.
Cost and longevity are also factors to consider. Seals are generally more expensive than gaskets due to their dynamic nature and specialized design. However, they tend to have a longer lifespan in applications where motion and friction are involved. Gaskets, on the other hand, are more cost-effective and suitable for static applications with lower wear and tear.
Furthermore, it is important to consider installation and maintenance requirements. Seals often require more precision during installation as they need to fit perfectly to prevent any leaks or failures. Gaskets, on the other hand, are easier to install and replace when necessary.
For systems requiring FDA compliance, selecting the appropriate type of gaskets and seals, such as those made from FDA-approved materials, is essential. That said, a good rule of thumb is to consult with a seal and gasket specialist or manufacturer to ensure that you select the right product for your specific application. They can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their expertise and knowledge of various seal and gasket materials, designs, and specifications.
Can you reuse seals and gaskets, or should they be replaced every time they're taken out?
Seals and gaskets are typically designed for single-use and should be replaced every time they're taken out. Reusing seals and gaskets may compromise their effectiveness and lead to leaks or other issues. It's always best to use new seals and gaskets for optimal performance and reliability.
Final Thoughts
In summary, selecting the right type of seals and gaskets, whether it's SBR for general use or specialized materials for specific needs, is crucial in ensuring system efficiency and reliability. Consider factors such as temperature and pressure ratings, cost, longevity, installation requirements, and maintenance before making a decision.
Remember that seals and gaskets are generally designed for single-use, so it's recommended to replace them every time they're taken out to avoid any potential problems. By making informed choices and prioritizing quality, you can enhance the performance and longevity of your system while minimizing the risk of leaks and other issues.
Finally, sign up on our website now to receive exclusive giveaways and special offers on equipment parts!